When you get a cut, your body heals itself by forming a blood clot over the wound to seal it. This keeps it safe from infections and bacteria, as well as keeping the rest of your blood inside. The ability of blood to clot, which is the responsibility of tiny blood cells called platelets, is lifesaving.
But when a blood clot forms in the wrong place (for example, inside your body), the effects can be dangerous and even deadly, especially because it's impossible to see one forming. So, if you can't see it, how can you know if you're in danger?
When a blood clot forms inside a blood vessel, it can block blood from accessing various parts of your body, causing pain, tissue damage, and even death.
A blood clot in one of your body's large veins, typically in the arms and legs, is called deep vein thrombosis (DVT), while a blood clot in the lungs is called a pulmonary embolism (PE).
A PE can cause death if not treated immediately. A DVT is less of an immediate emergency, but if left untreated, the clot can travel to the lungs and become a deadly PE.
The good news, though, is that you can know the risk factors and the symptoms of blood clots. Being aware of these signs can alert you if something is wrong, and can help you make adjustments to stay healthy.
Read on to learn the risk factors and the symptoms of blood clots. If you recognize any of these in yourself of someone you know, tell a doctor immediately.
Thumbnail Photos: Wikimedia Commons, Flickr
What Is A Blood Clot, And What Can It Do To Your Body?
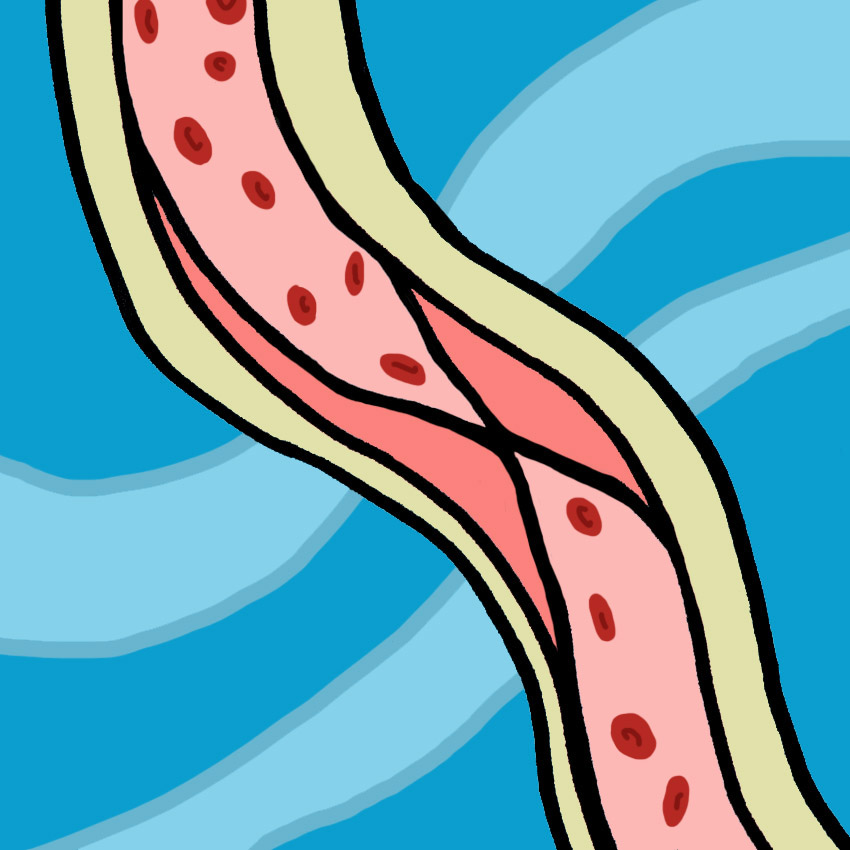
A blood clot, technically known as a "thrombus," is a chunk of congealed blood inside a blood vessel.
While blood clotting on the outside of your body is normal and healthy, a clot inside your body is not.
Blood clots typically form against the wall of an artery or vein, or agains the valve of a vein. They can happen when internal tissues experience physical trauma and abnormal blood flow, or if the blood becomes thickened and has a higher chance to coagulate, as happens with certain types of cancers.
These clots can lead to a stroke, a heart attack, and blockage of the lungs. They can also cause tissue damage and tissue death and even be fatal.
What Puts You At Risk For Blood Clots? Risk #1: Being Over 65

A blood clot can appear in anyone's body, regardless of age, but the risk increases as you get older. The risk is higher after the age of 65.
It's especially true for those who spend a lot of time inactive or who have limited mobility.
Risk #2: Recent Injury Or Surgery
When your body is trying to repair itself from a wound, including one created by surgery, your blood will be clotting all over the place. Sometimes, one of these clots can end up somewhere it shouldn't.
The risk can also be exacerbated by long periods of bed rest or wheelchair use during recovery time. Doctors, of course, know about this, so you may find they'll want to take measures to prevent clots.
Certain cancers, including leukemia, will also make your blood more likely to coagulate, which can lead to a higher risk of blood clots.
Risk #3: Pregnancy

The hormonal and physical changes in your body during pregnancy can lead to a risk of blood clots, as can the added baby weight.
In fact, pregnancy is one of the leading causes of blood clots in younger people.
The risk is present for women who have recently given birth, too. This happens while their body heals from the childbirth process, whether the delivery was natural or via C-section.
Risk #4: Hormonal Birth Control Or Estrogen

Women taking hormonal birth control, as well as people taking estrogen, are at a higher risk for blood clots.
Hormonal birth control uses the same hormones that appear during pregnancy, and elevated amounts of these hormones increase the risk of blood clotting.
Being young, healthy, and active will drive the risk down. Age, inactivity, and smoking will increase it further (and you shouldn't smoke anyway!).
Risk #5: Family History
A family history of deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolisms, circulation issues, or problems with blood clots will increase your risk, too.
This doesn't mean you'll definitely get one, but it does mean you'll have to remember it when considering things like birth control or hormone therapy, as well as diet and exercise habits. You should also let your doctor know about it, especially if surgeries are involved.
If you are concerned that you might be at risk, you should also know the symptoms of a blood clot.
What Are The Signs Of A Blood Clot? Symptom #1: Chest Pain When Inhaling Deeply

Pain during breathing could be a sign of a clot, especially if the pain increases when you draw a deep breath, or if the pain makes breathing regularly difficult. You may also feel pain when coughing.
In addition to difficulty breathing, the breath might also come rapidly. If this happens, seek medical attention immediately, as it means oxygenated blood is being denied to the lungs and the left side of the heart.
Symptom #2: Redness And Warmth Of The Skin
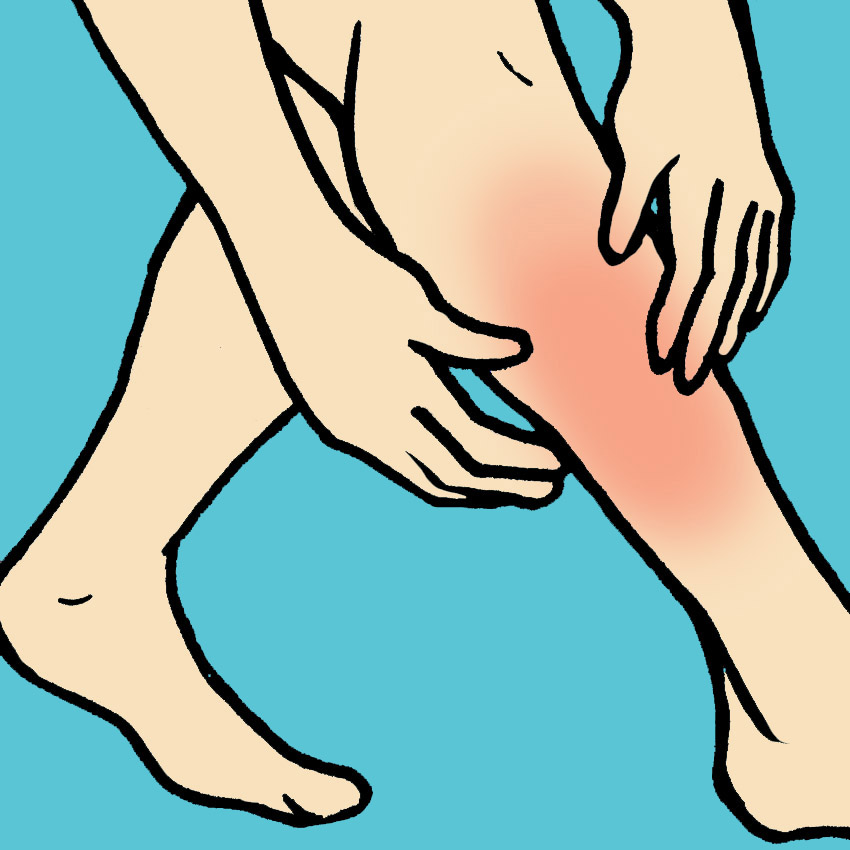
If your skin feels hot and looks flushed in only one specific area, usually the arm or leg, deep vein thrombosis may be to blame.
However, this can also happen as a result of many other medical issues. If you're worried, check with a doctor to see what's really going on.
Symptom #3: Rapid Heartbeat

As oxygenated blood is being denied to the lungs, the heart rate increases. If your heart suddenly starts pounding, and especially if it's accompanied by low blood pressure and dizziness or fainting, call an ambulance immediately.
This increase in heart rate may not be painful, but it is dangerous nonetheless.
Symptom #4: Coughing With Blood

Anytime you cough up blood is cause for alarm, and it's a very common sign of a pulmonary embolism. If you see blood after coughing, go to the hospital — don't wait!
Symptom #5: Soreness And Swelling
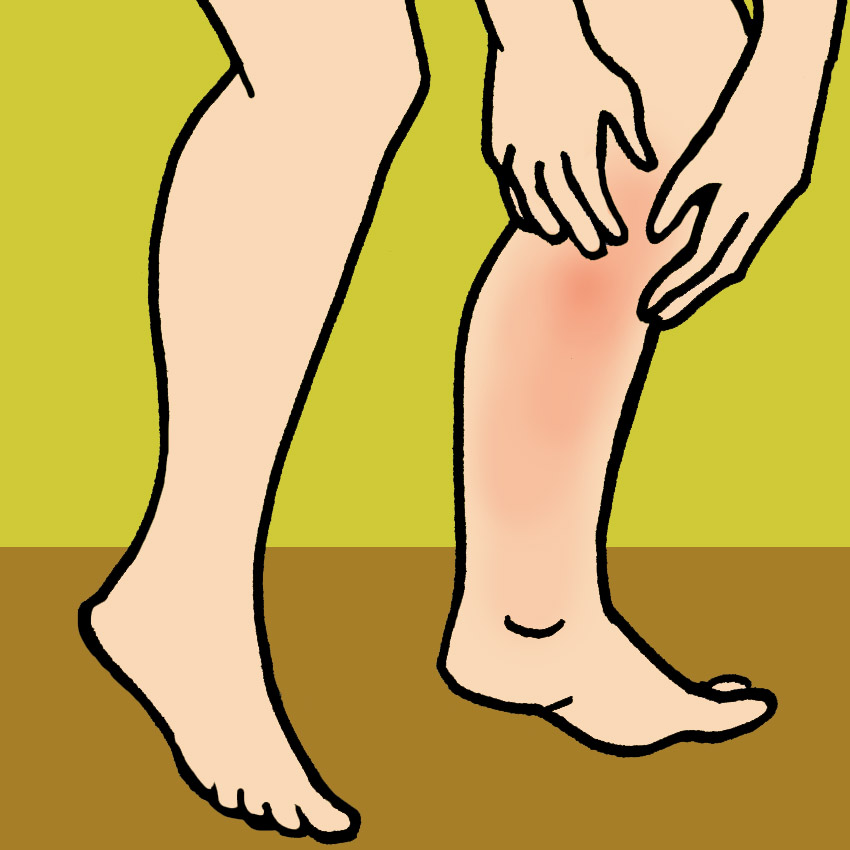
If blood is blocked, it can pool in one area of a limb, causing swelling and heaviness. On the other hand, if blood is being denied to a limb, you may experience swelling and numbness.
In very severe cases, blood flow is cut off completely. The skin can take on a bluish tinge and the oxygen-deprived tissue will start to die.
What Should You Do If You Think You Have One Of These Symptoms?
Blood-clot symptoms, especially PE symptoms, typically appear suddenly.
If you experience any of them, get medical attention immediately.
You may have to go to the emergency room, but acting quickly can save your life. As dangerous as they are, blood clots are treatable.
SHARE this important information with everyone you know, and learn more at Stop the Clot.




