When it comes to our health, it can be easy to ignore symptoms for a while and hope that they'll go away.
After all, most women I know will do whatever it takes to make sure the people in their lives get medical care, myself included, but when it comes to our own bodies? We rub some dirt on it and move on.
Unfortunately, being stoic about your aches and pains can land you in deep trouble at the doctor's office later.
Same goes for any and all "female trouble." Whether you just have some cramps, or you're experiencing scarier symptoms, it's always worth getting a check-up, because some conditions hide for a long time.
Ovarian torsion is a great example of something you want to nip in the bud; it causes mild, easily mistaken symptoms for a long while, before suddenly turning into a major medical problem.
Scroll through below to learn the symptoms every woman needs to watch out for.
Photo Credit: Wikimedia Commons
What Is A Twisted Ovary?
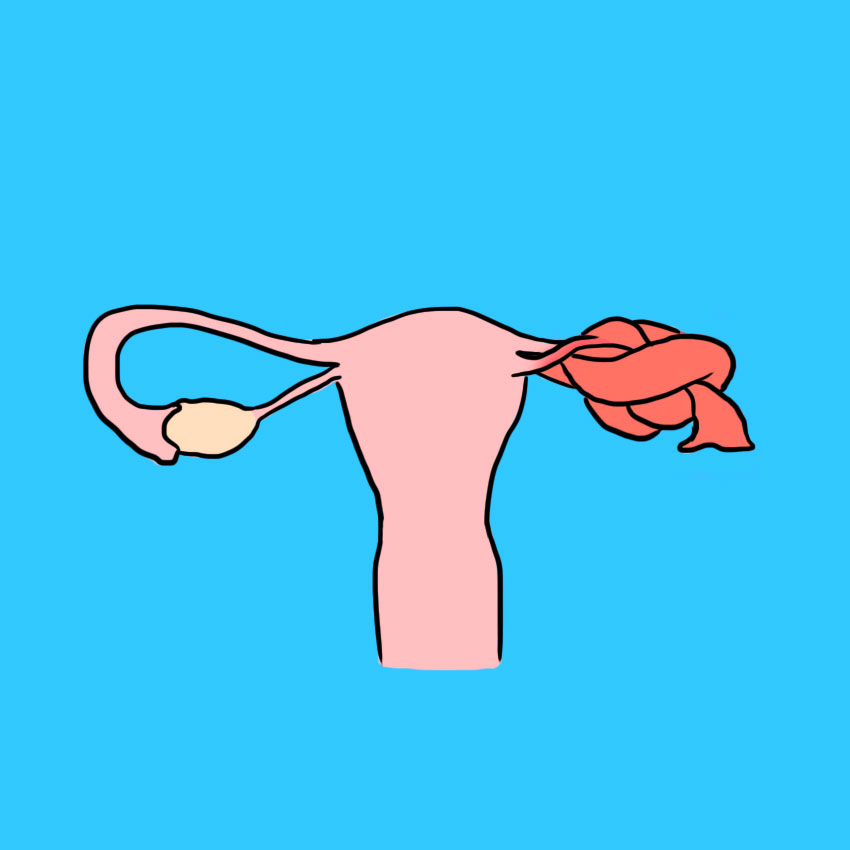
Your ovaries are the two small sacs on either side of your uterus that produce your eggs.
Twisted ovary, also known as ovarian or adnexal torsion, is when one of your ovaries flops out of place and twists around.
Your ovary is held in place by ligament and muscle, so if your ovary twists, all of the ligaments (and sometimes the fallopian tube) will be twisted as well, which causes intense pain.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Twisted Ovary? Sign #1: Crampy Pain And Spotting
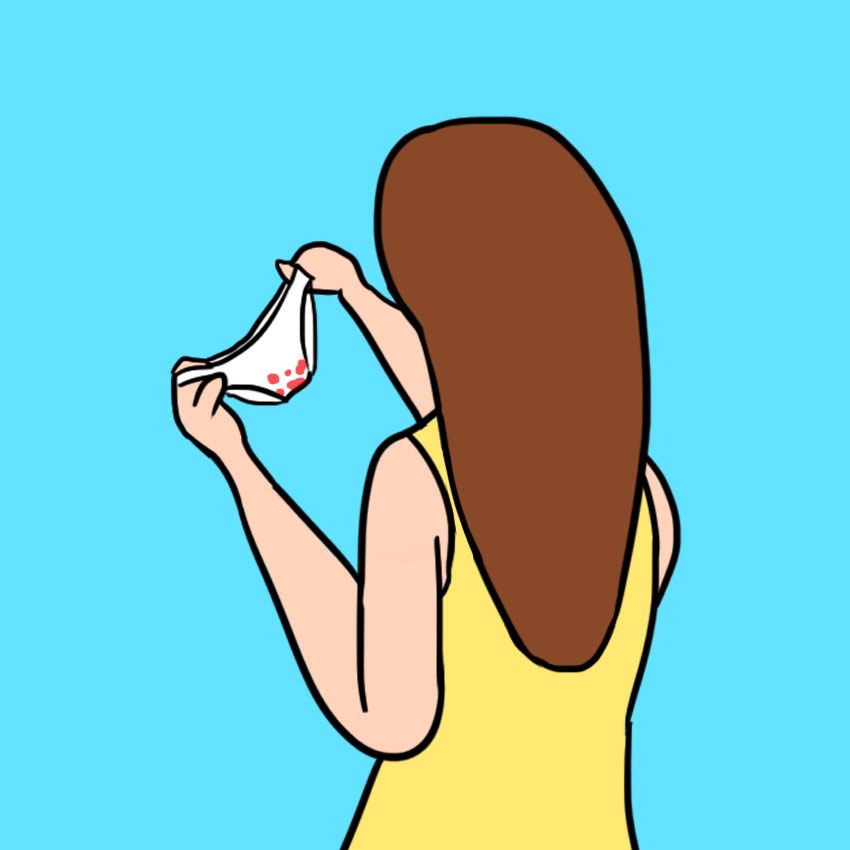

One of the early warning signs of ovarian torsion is a crampy pain that comes with spotting.
When your ovary starts to flag on one side or the other, you might feel cramping in your uterus, and on one side of your abdomen.
Your body may also begin to shed some of its uterine lining, which can cause spotting, even if your period isn't due.
Sign #2: Tenderness In Your Belly
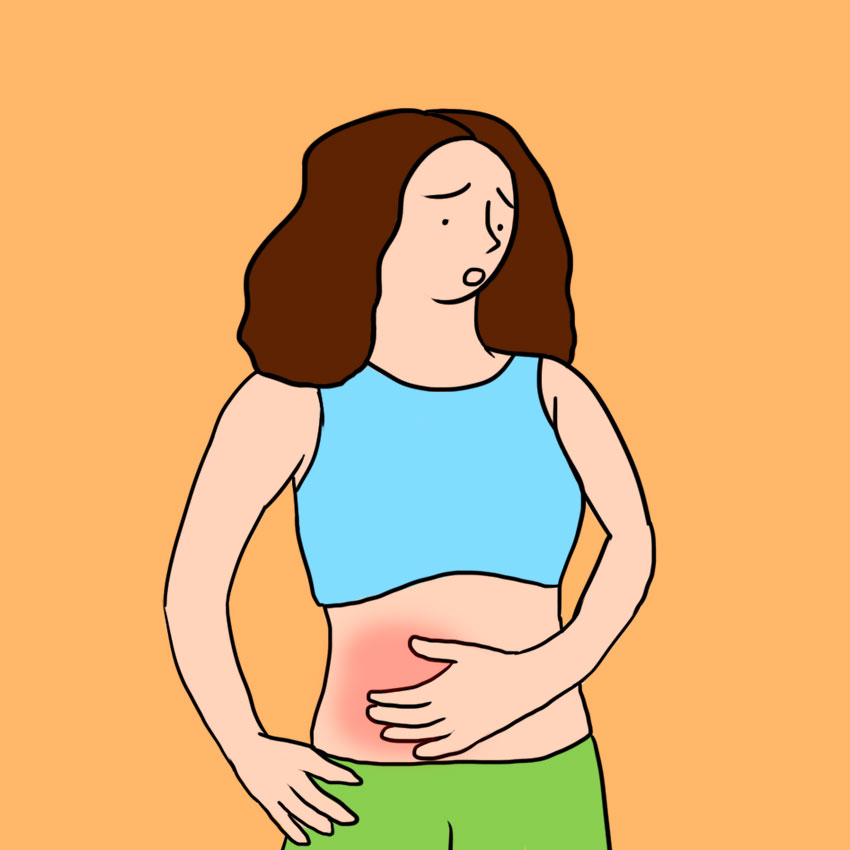
It's likely, before an ovarian torsion, you'll also experience bloating and tenderness in your lower abdomen, which might also be focused on just one side.
The cramping and tenderness in your belly may come and go, which could indicate that your ovary is swinging slightly back and forth on the ligaments that support it, without fully twisting around.
Sign #3: Severe Lower Abdominal Pain
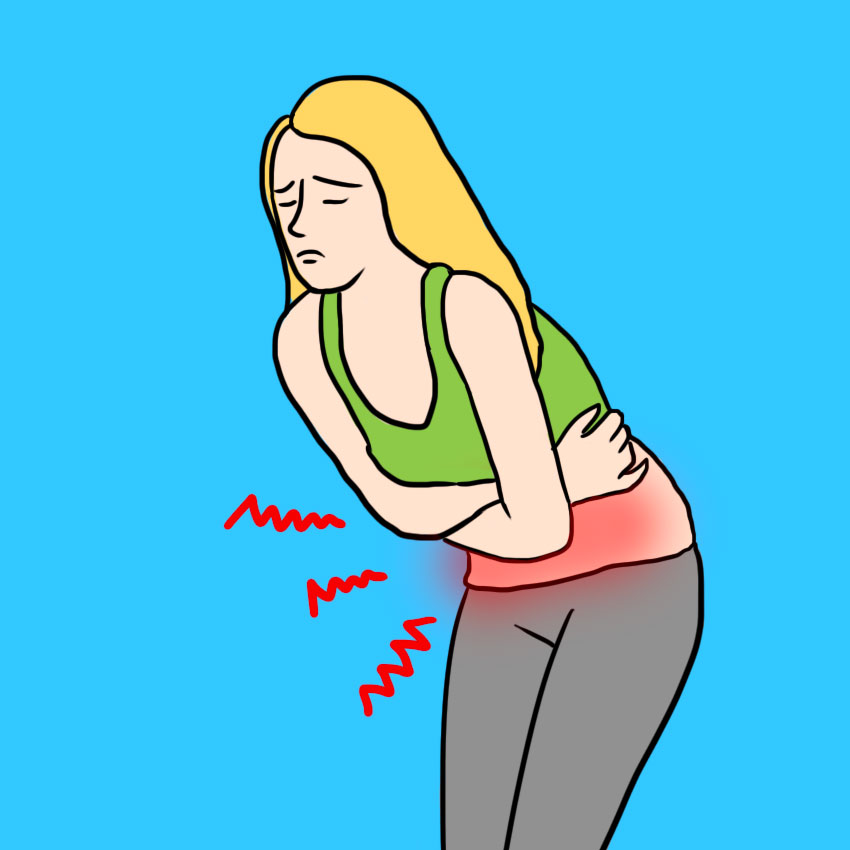

If your ovary fully twists on the ligaments, you will feel a sudden, sharp pain on one side.
This is partially because the ovary is tugging on the ligaments, and partially because the torsion has cut off the blood flow to and from the organ.
Ovarian torsion is more common on the right side of your body, so it can be mistaken for appendicitis at first.
Either way, go straight to the ER, because this kind of pain indicates a medical emergency.
Sign #4: Nausea & Vomiting
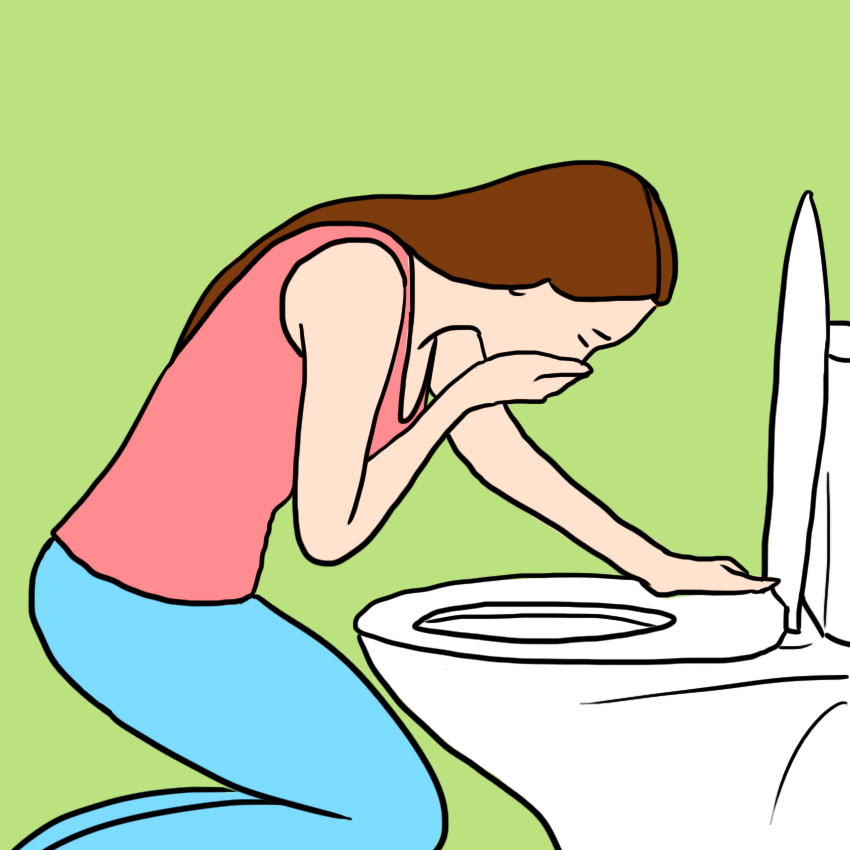

Along with intense stomach pain, a full-on ovarian torsion may cause a lot of nausea and vomiting.
This is a natural bodily response to pain and to abdominal discomfort.
However, it's easy to mistake a bout of vomiting and stomach pain for an ordinary bug, so watch out for menstrual symptoms that coincide, since that's often the hallmark of a torsion.
What Can Cause A Twisted Ovary? Cause #1: Cysts
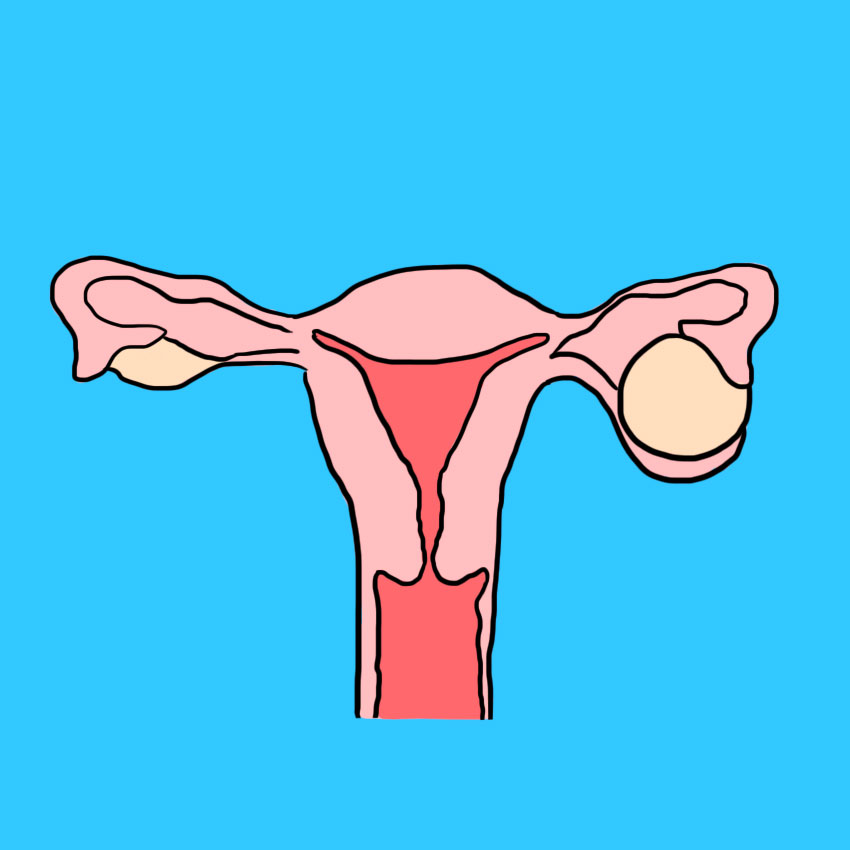
Cysts are the number one cause of twisted ovary, and they're pretty common.
An ovarian cyst is a solid, fluid-filled sac that develops on the outside of the ovary, often in response to hormonal fluctuations.
Usually, they're harmless, but they can be very painful, and can become dangerous if they rupture or weigh your ovary down enough that it twists.
Cause #2: Fertility Treatment
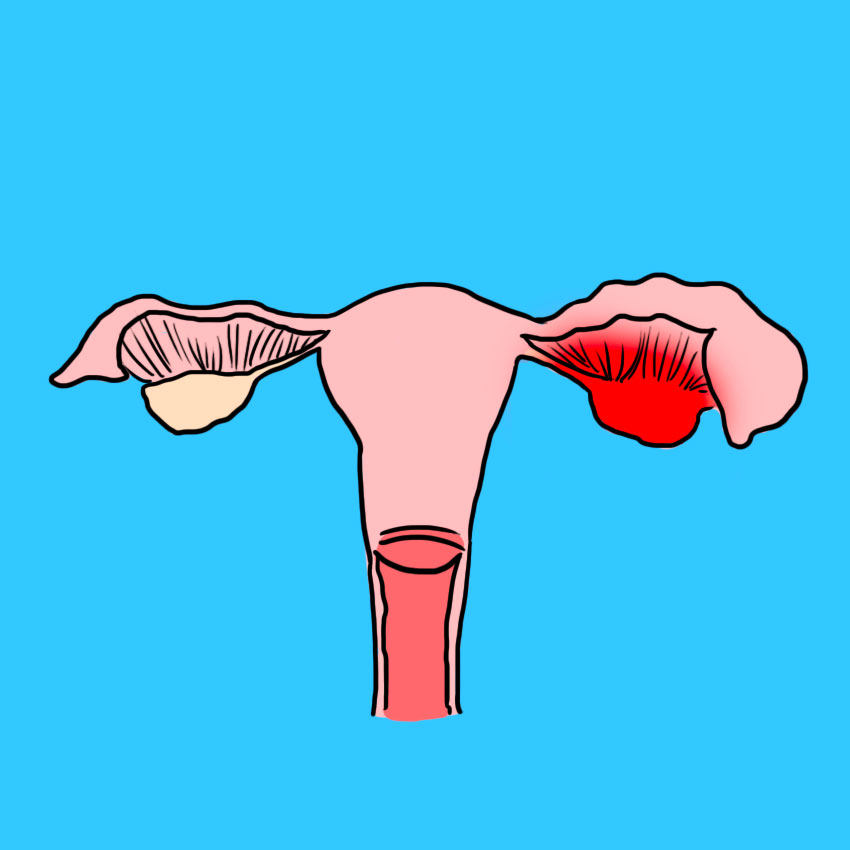
There are lots of different fertility treatments out there, but many of the common treatments focus on stimulating the ovarian follicle with hormones to produce an egg.
Fertility treatments encourage ovulation by making the ovaries swell and grow bigger, which makes them heavier.
Heavier ovaries are at a higher risk for twisting, so some doctors will recommend low-impact exercise to help avoid torsion during fertility treatments.
Cause #3: Tumor
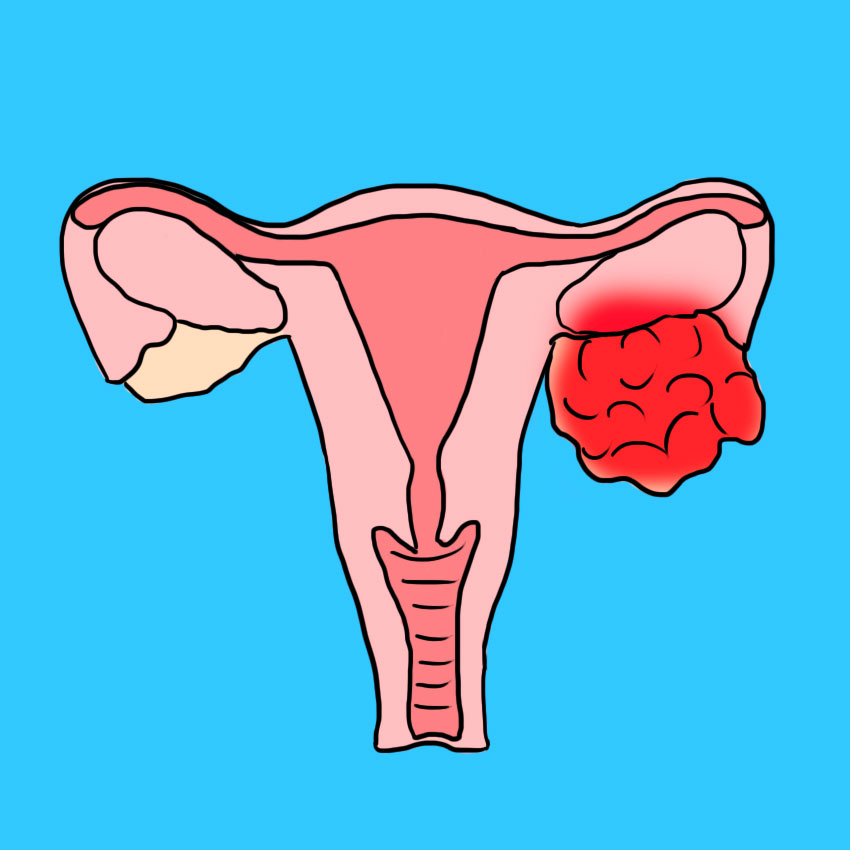
In some rare cases, ovarian torsion might be your first indication that a tumor is growing on your ovary.
Much like a cyst, tumors can start developing on the ovaries and weigh them down, leading to a twist.
Ovarian tumors can be benign or cancerous, but in many cases, the whole ovary will need to be removed to perform a biopsy to check for cancer.
Cause #4: Physiology
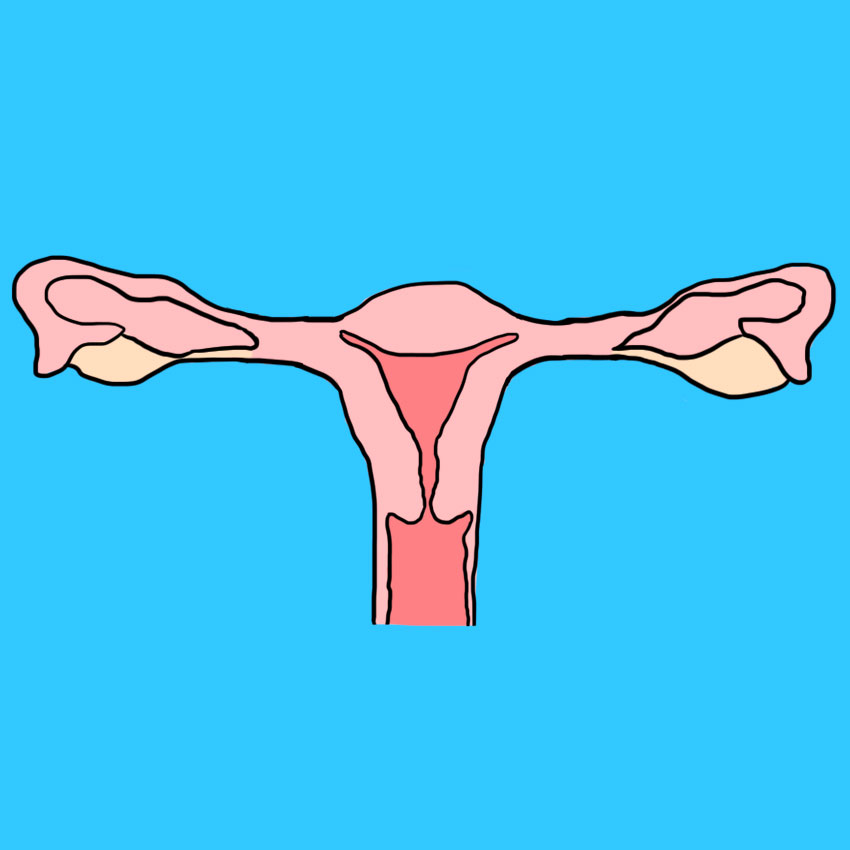
Some people are simply more prone to twisted ovaries; it's just luck of the draw.
If you happen to have longer fallopian tubes, or particularly heavy ovaries, you are also more likely to suffer a torsion at some point.
On the rare occasions an ovarian torsion happens in a child or elderly person, it's usually due to physiology.
If you were surprised by the story behind twisted ovaries, SHARE this list with every woman you know.




