When I was little, I always loved watching movies that ended with happy couples living their lives together. Whether that was Cinderella and her prince or the parents in The Parent Trap, I dreamed of one day falling in love like they do.
Being romantic with another person can be exciting and enjoyable. Finding intimacy with someone is an exciting part of adult life. And of course, most people really enjoy having sex.
Having sex has a lot of benefits. It can relieve stress, release endorphins, make you feel closer to your partner, and even boost your memory!
But have you ever wondered about what exactly happens to your body during sex?
Most of us know that our heart beats a little faster, our adrenaline starts pumping, and our bodies react to our partner. This is known as the sexual response cycle.
Read below to find out more about the specifics of what happens to your body during sex!
Thumbnail Photo: Wikimedia / rt69
Phase 1: Excitement 1. Your Muscles Tense Up

In the first phase of the sexual response cycle, which can last minutes to hours, your muscles begin to tense up, explains the Cleveland Clinic.
During this phase, your body may feel more energized.
2. Your Heart Rate And Breathing Accelerate

In the excitement phase, your breathing and heart rate will speed up.
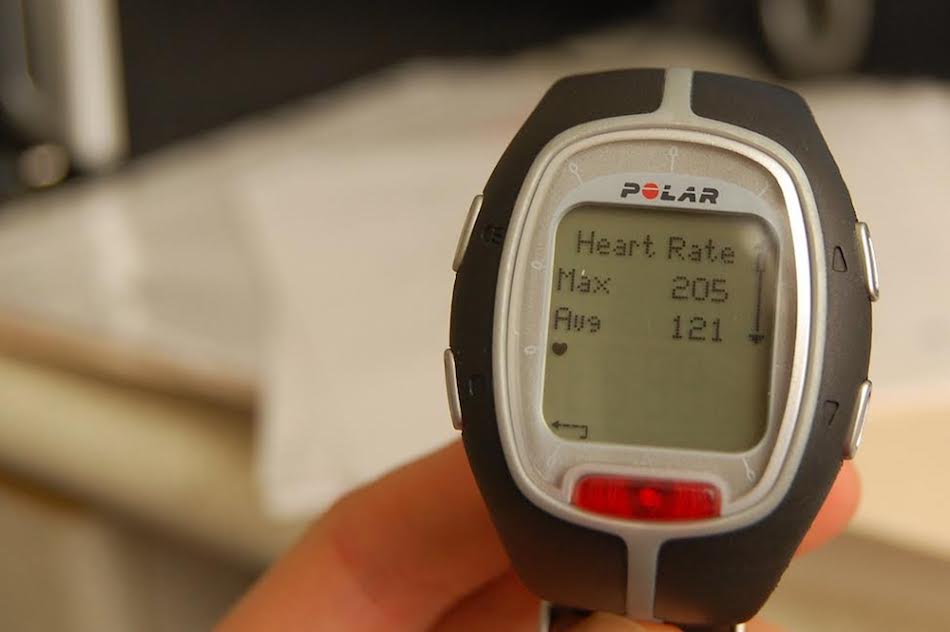

Your blood will start pumping through your body, which can also make you feel warmer.
With this increased blood flow, extra blood starts to make its way to the genitals.
3. Your Skin Becomes Flushed
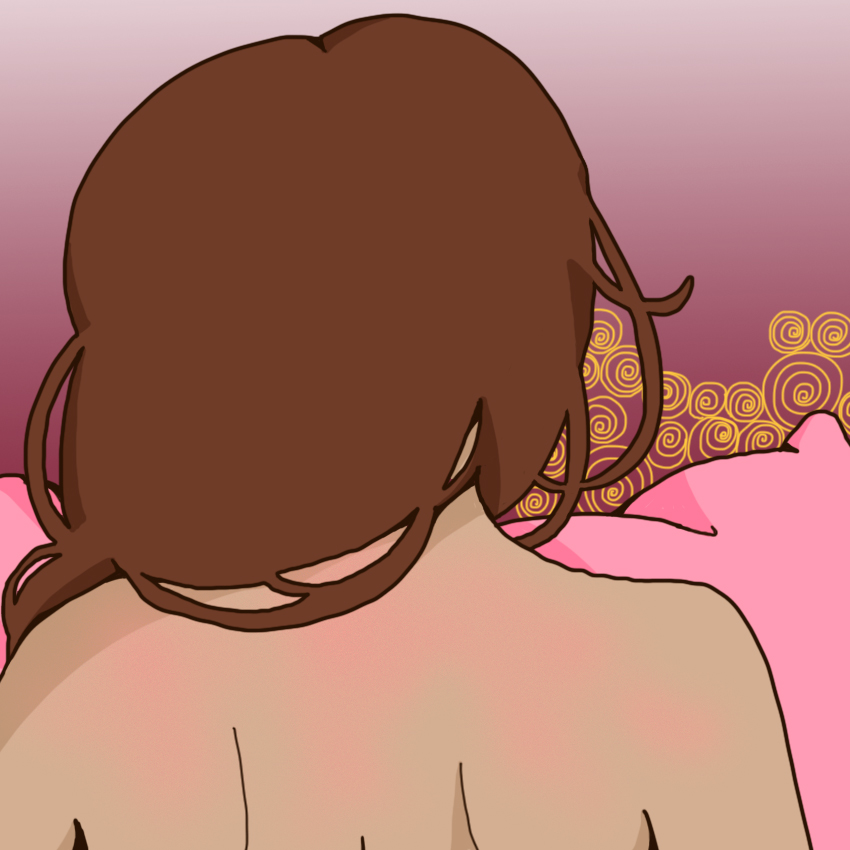
As your blood floods through your body, your skin may become flushed.

No makeup is necessary for the rosy glow of pink or red might appear on your back or chest.
At this time, your nipples will also become hard, and your breasts become fuller.
Phase 2: Plateau 4. Your Dopamine And Epinephrine Levels Rise

The plateau stage, which lasts right up until orgasm, intensifies the changes from the excitement phase.
During this second phase, levels of dopamine (the feel-good chemical) and epinephrine (adrenaline) increase in your body.
5. Your Muscles May Start Spasming
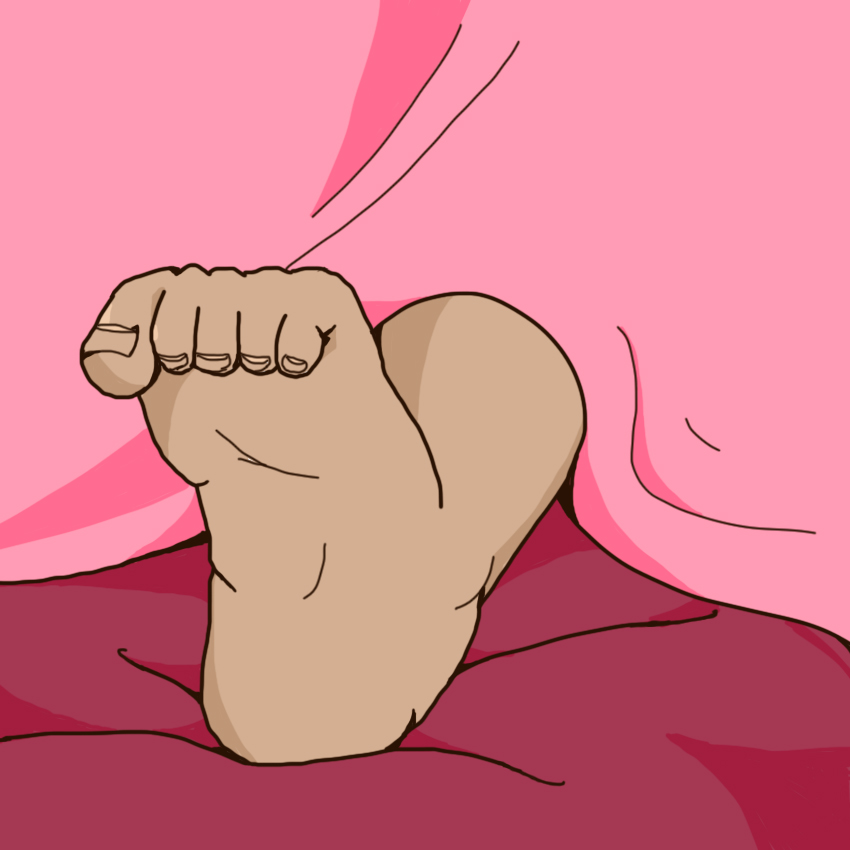

The muscle tension that began in the excitement phase continues to build, causing some muscles to start spasming.
Typically, muscle spasms in this stage will occur in the face, hands, and feet.
Phase 3: Orgasm 6. Your Muscles Involuntarily Contract

The orgasm phase, which is probably the most well-known phase of sex, is the climax of intercourse.
Orgasm is the shortest phase of the sexual response cycle and usually only lasts a few seconds.

All the tension that has built up in your muscles during the previous phases finally comes to a head in this phase, and your muscles start contracting involuntarily.
The muscle spasms carry to your vagina, where rhythmic contractions occur.
7. Your Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, And Breathing Hit A Peak

Blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing, which have all been ramping up throughout the course of sex, finally hit a peak.
Your body rapidly takes in oxygen during the orgasm phase.
8. Your Oxytocin Production Increases

During this phase of sex, oxytocin (the feel-good neurotransmitter) increases by a lot. It rises throughout all phases of sex, but it boosts a ton during orgasm.
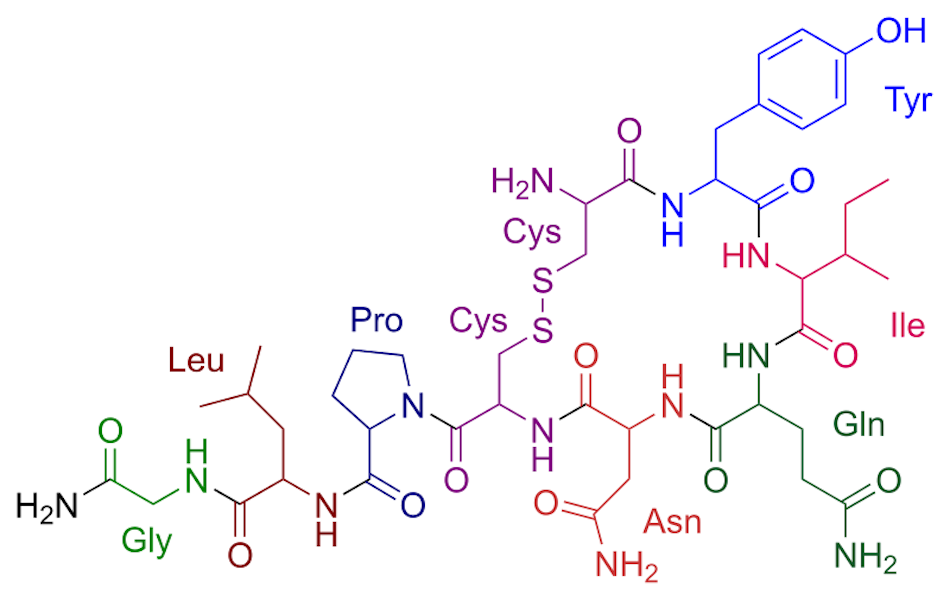
Oxytocin can also improve your pleasure sensations.
Phase 4: Resolution 9. Everything Goes Back To Normal
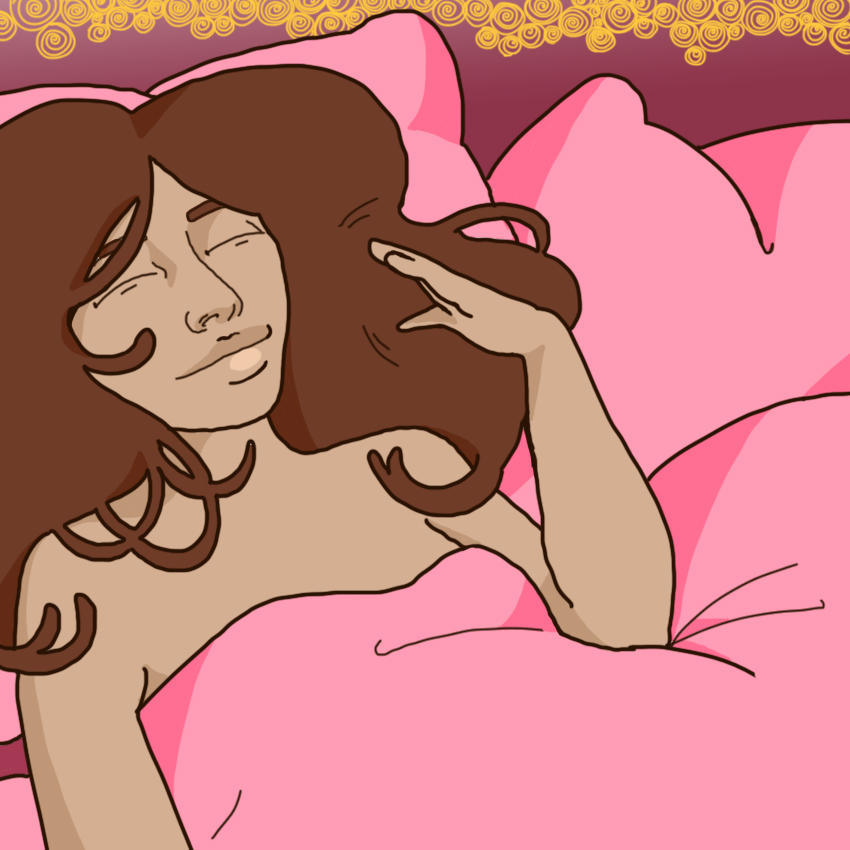
The final phase of the sexual response cycle is resolution.
This is when your body starts to return to normal — any swollen body parts return to their usual size and color, and your breathing and heart rate slow back down.
Many people feel an increased sense of emotional intimacy during this phase.
If you think everyone should know more about sex, please SHARE this article with your friends!




